 West Nile virus (WNV) is most commonly transmitted to humans by mosquitoes. You can reduce your risk of being infected with WNV by using insect repellent and wearing protective clothing to prevent mosquito bites. There are no medications to treat or vaccines to prevent WNV infection. Fortunately, most people infected with WNV will have no symptoms. About 1 in 5 people who are infected will develop a fever with other symptoms. Less than 1% of infected people develop a serious, sometimes fatal, neurologic illness.
West Nile virus (WNV) is most commonly transmitted to humans by mosquitoes. You can reduce your risk of being infected with WNV by using insect repellent and wearing protective clothing to prevent mosquito bites. There are no medications to treat or vaccines to prevent WNV infection. Fortunately, most people infected with WNV will have no symptoms. About 1 in 5 people who are infected will develop a fever with other symptoms. Less than 1% of infected people develop a serious, sometimes fatal, neurologic illness.
The symptoms of neurologic illness can include headache, high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, coma, tremors, seizures, or paralysis.
Serious illness can occur in people of any age. However, people over 60 years of age are at the greatest risk for 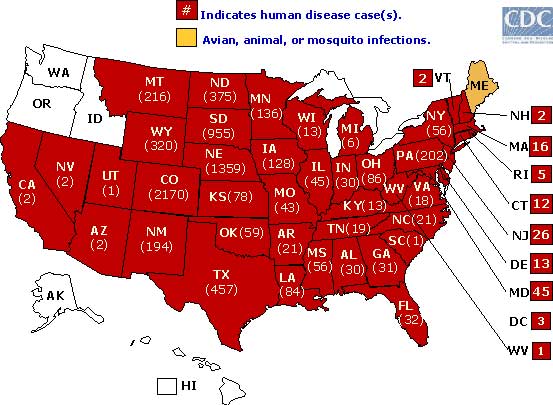 severe disease. People with certain medical conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, hypertension, kidney disease, and people who have received organ transplants, are also at greater risk for serious illness.
severe disease. People with certain medical conditions, such as cancer, diabetes, hypertension, kidney disease, and people who have received organ transplants, are also at greater risk for serious illness.
Recovery from severe disease may take several weeks or months. Some of the neurologic effects may be permanent. About 10 percent of people who develop neurologic infection due to West Nile virus will die.
Currently, no vaccine or specific antiviral treatments for West Nile virus infection are available. Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to reduce fever and relieve some symptoms. And in severe cases, patients often need to be hospitalized to receive supportive treatment, such as intravenous fluids, pain medication, and nursing care.
Source: CDC
